SYNOPSIS
DESCRIPTION
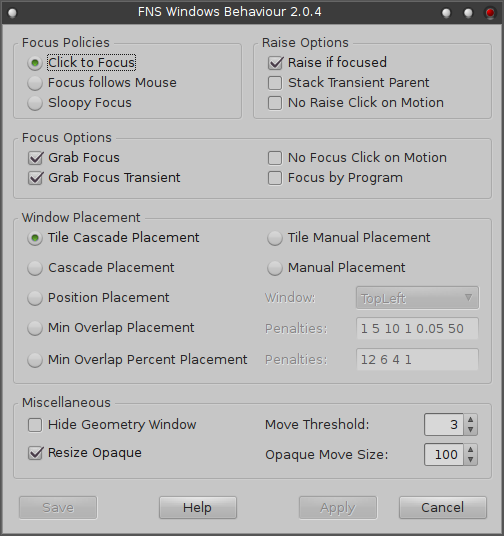
FNS-WindowsBehaviour is used to configure some of the window behaviours in Fvwm-Nightshade.
The following option descriptions are copied from Fvwm’s manpage because there is all described as better as we already can.
On the other hand it is easier to find a passage in Fvwm’s huge manpage while searching.
OPTIONS
Focus Policies
- Click to Focus
-
ClickToFocus instructs fvwm to give the focus to a window when it is clicked in.
- Focus follows Mouse
-
FocusFollowsMouse tells fvwm to give a window the focus as soon as the pointer enters the window, and take it away when the pointer leaves the window.
- Sloopy Focus
-
SloppyFocus is similar, but doesn’t give up the focus if the pointer leaves the window to pass over the root window or a ClickToFocus window (unless you click on it, that is), which makes it possible to move the mouse out of the way without losing focus.
Raise Options
- Raise if focused
-
Controls if the window is raised when focused (depending on the focus model).
- Stack Transient Parent
-
The StackTransientParent style augments RaiseTransient and LowerTransient styles. Raising a window with StackTransientParent style transfers the raise action to the main window if the window being raised is a transient and its main window has RaiseTransient style; this effect makes raise on a transient act just like raise on its main - the whole group is raised. Similar behavior holds for lowering a whole group of transients when the main has LowerTransient style. DontStackTransientParent turns this behavior off. (Dont)StackTransientParent has no effect if RaiseTransient and LowerTransient are not used.

A window with the RaiseTransient style that has transient windows raises all its transients when it is raised. The DontRaiseTransient style disables this behavior. All windows are then treated as if they had no transients.
A window with the LowerTransient style that has transient windows lowers all its transients when it is lowered. The DontLowerTransient style disables this behavior. All windows are then treated as if they had no transients.
If StackTransientParent is set the following style combination is used:
Style * RaiseTransient Style * LowerTransient Style * StackTransientParent
If StackTransientParent is disabled this style combination is used:
Style * DontRaiseTransient Style * DontLowerTransient Style * DontStackTransientParent
- No Raise Click on Motion
-
If the FPIgnoreRaiseClickMotion style is used, clicking in a window and then dragging the pointer with the button held down does not count as the click to raise the window. Instead, the application processes these events normally. This is useful to select text in a terminal window with the mouse without raising the window. However, mouse bindings on the client window are not guaranteed to work anymore (see Mouse command. Note that this style forces that the initial click is passed to the application. The distance that the pointer must be moved to trigger this is controlled by the MoveThreshold command.
The MoveThreshold can be set in the Miscellaneous section.
Focus Options
- Grab Focus and Grab Focus Transient
-
New normal or transient windows with the GrabFocus (FPGrabFocus + FPReleaseFocus) or GrabFocusTransient (FPGrabFocusTransient + FPReleaseFocusTransient) style automatically receive the focus when they are created. GrabFocus is the default for windows with the ClickToFocus style. Note that even if these styles are disabled, the application may take the focus itself. Fvwm can not prevent this.

FPReleaseFocus and FPReleaseFocusTransient controls whether the focus is returned to another window when the window is closed. Otherwise no window or the window under the pointer receives the focus.
- No Focus Click on Motion
-
If the FPIgnoreFocusClickMotion style is used, clicking in a window and then dragging the pointer with the button held down does not count as the click to focus the window. Instead, the application processes these events normally. This is useful to select text in a terminal window with the mouse without raising the window. However, mouse bindings on the client window are not guaranteed to work anymore (see Mouse command). This style forces the initial click to be passed to the application. The distance that the pointer must be moved to trigger this is controlled by the MoveThreshold command.
The MoveThreshold can be set in the Miscellaneous section.
- Focus by Program
-
The FPFocusByProgram style allows windows to take the focus themselves.
Window Placement
Applications can place windows at a particular spot on the screen either by window manager hints or a geometry specification. When they do neither, then the window manager steps in to find a place for the window. Fvwm knows several ways to deal with this situation. The default is TileCascadePlacement.
- Tile Cascade Placement
-
TileCascadePlacement automatically places new windows in a smart location - a location in which they do not overlap any other windows on the screen. If no such position can be found CascadePlacement is used as a fall-back method.
- Tile Manual Placement
-
This is the same as TileCascadePlacement, but uses ManualPlacement as the fall-back method.
- Cascade Placement
-
CascadePlacement automatically place new windows in a cascading fashion.
- Manual Placement
-
Aka active placement. The user is required to place every new window manually. The window only shows as a rubber band until a place is selected manually. The window is placed when a mouse button or any key except Escape is pressed. Escape aborts manual placement which places the window in the top left corner of the screen. If mouse button 2 is pressed during the initial placement of a window (respectively Shift and mouse button 1 in case Mwm emulation has been enabled with the Emulate command), the user is asked to resize the window too.
- Position Placement
-
When used with TopLeft argument, new windows are placed in the top left corner of the display. With the argument Center, all new window appear at the center of the screen, and with UnderMouse, windows are centered under the mouse pointer where possible. If the window is unable to fit on the screen because the pointer is at the edge of the screen, then the window is forced on-screen using this option.
- Min Overlap Placement
-
MinOverlapPlacement automatically places new windows in a location in which the overlapping area in pixels of other windows is minimized. By default this placement policy tries to avoid overlapping icons and windows on higher layers. This can be configured with the Penalties (MinOverlapPlacementPenalties style).
MinOverlapPlacementPenalties takes at most 6 positive or null decimal arguments:
normal ontop icon sticky below strut
if trailing arguments are missing the default is used which is:
1 5 10 1 0.05 50
The normal factor affects normal windows, the ontop factor affects windows with a greater layer than the window being placed, the icon factor affects icons, the sticky factor affects sticky windows, the below factor affects windows with a smaller layer than the window being placed, the strut factor affects the complement of the EWMH working area if the window being placed has the EWMHPlacementUseWorkingArea style and windows with an EWMH strut hint (i.e., a "please do not cover me" hint) if the window being placed has the EWMHPlacementUseDynamicWorkingArea style.
These factors represent the amount of area that these types of windows (or area) are counted as, when a new window is placed. For example, by default the area of ontop windows is counted 5 times as much as normal windows. So MinOverlapPlacement (and MinOverlapPercentPlacement described below) covers 5 times as much area of another window before it will cover an ontop window. To treat ontop windows the same as other windows, set this to 1. To really, really avoid putting windows under ontop windows, set this to a high value, say 1000. This style affects the window already mapped and not the window which is currently placed.
There is one exception to this rule: in the case of the window being placed has the EWMHPlacementUseWorkingArea style the strut factor affects the placed window.
- Min Overlap Percent Placement
-
MinOverlapPercentPlacement is similar to MinOverlapPlacement but tries to minimize the overlapped percentages of other windows instead of the overlapped area in pixels. This placement policy tries to avoid covering other windows completely and tries even harder not to cover small windows. This can be configured with the Penalties (MinOverlapPercentPlacementPenalties styles).
MinOverlapPercentPlacementPenalties takes at most 4 positive or null integer arguments:
cover_100 cover_95 cover_85 cover_75
if trailing arguments are missing the defaults are used which are:
12 6 4 1
The cover_xx factor is used when the window being placed covers at least xx percent of the window. This factor is added to the factor determined by the MinOverlapPlacementPenalties style.
Miscellaneous
- Hide Geometry Window
-
Hides the position or size window that is usually shown when a window is moved or resized interactively.
- Resize Opaque
-
ResizeOpaque instructs fvwm to resize the corresponding windows with their contents visible instead of using an outline. Since this causes the application to redraw frequently it can be quite slow and make the window flicker excessively, depending on the amount of graphics the application redraws. The ResizeOutline style (default) negates the ResizeOpaque style. Many applications do not like their windows being resized opaque, e.g. XEmacs, Netscape or terminals with a pixmap background. If you do not like the result, do not use the ResizeOpaque style for these windows. To exempt certain windows from opaque resizing you could use these lines in your configuration file:
Style * ResizeOpaque Style rxvt ResizeOutline Style emacs ResizeOutline
- Move Threshold
-
When the user presses a mouse button upon an object fvwm waits to see if the action is a click or a drag. If the mouse moves by more than pixels pixels it is assumed to be a drag.
Previous versions of fvwm hardwired pixels to 3, which is now the default value. If pixels is negative or omitted the default value (which might be increased when 16000x9000 pixel displays become affordable) is restored.
- Opaque Move Size
-
Tells fvwm the maximum size window with which opaque window movement should be used. The percentage is percent of the total screen area (may be greater than 100). With 0 all windows are moved using the traditional rubber-band outline. With 100 all windows are moved as solid windows. The default is 5 which allows small windows to be moved in an opaque manner but large windows are moved as rubber-bands.
FILES
The settings are saved in ~/.fvwm-nightshade/.users. In this file the user can put her/his custom changes, too.
AUTHOR
© 2015 - 2016 Thomas Funk <t.funk@web.de>
 Features
Features News/Blog
News/Blog News
News Blog
Blog Screenshots
Screenshots Documentation
Documentation FAQ
FAQ Installation/Deinstallation
Installation/Deinstallation Dependencies
Dependencies Uninstall Fvwm-Nightshade
Uninstall Fvwm-Nightshade Tips
Tips Usage
Usage First Start
First Start FNS-BaseSetup
FNS-BaseSetup FNS-WindowsBehaviour
FNS-WindowsBehaviour Desktop Organisation
Desktop Organisation Root Menu
Root Menu FNS-MenuConfigurator
FNS-MenuConfigurator FNS-MenuBuilder
FNS-MenuBuilder Bindings
Bindings FNS-CompConfigurator
FNS-CompConfigurator FNS-CpuPerformance
FNS-CpuPerformance Configuration
Configuration Location of Files
Location of Files Startup
Startup Autostart
Autostart Advanced
Advanced Debugging
Debugging Tools
Tools Theme Creation
Theme Creation Layout Creation
Layout Creation Language Creation
Language Creation Module Creation
Module Creation SimpleGtk2
SimpleGtk2 Get Involved
Get Involved Development
Development Contact
Contact About
About Downloads
Downloads